Overview
This project represents a tangible expression of my passion for large-scale, real-time online games and my engineering background building distributed systems at scale. My goal was to design and implement an end-to-end live-service framework capable of supporting the architecture, runtime behavior, and operational demands of a modern multiplayer title.
Rather than focus on a single subsystem, I set out to build the full software development stack: an Unreal Engine game client, a highly scalable microservice backend, a global-ready data layer, automated CI/CD pipelines, Kubernetes orchestration, observability infrastructure, and the tooling required to test, validate, and push the system toward global scale workloads.
The end result is a functioning live-service ecosystem that mirrors the architectural principles, engineering discipline, and runtime characteristics expected in production environments. The system supports real-time interactions over TCP, scalable microservices with Go, regional deployments, global databases with CockroachDB, payments with Stripe, Inventory, Cosmetics, Progression, and a full observability suite with Grafana and Prometheus for diagnosing performance, latency, and system health.
The Challenge
The core challenge I set for myself was simple to articulate but extremely demanding to execute: Could I, as one engineer, build a fully scalable, globally capable live-service architecture from scratch that could realistically support tens of thousands of concurrent players?
To answer this, I needed to solve a set of problems that normally require large teams:
- Design a real-time communication layer between Unreal Engine and backend services with predictable latency and high throughput.
- Architect a microservice ecosystem for global scale that remains resilient to partial failures, and scales horizontally.
- Simulate the scale of tens of thousands of players without access to a large pool of resources.
- Build an observability stack for latency, throughput, service health, and distributed tracing.
- Global scale database storage with regional clusters, and player state consistency.
- Integrate monetization and persistent progression in a way that feels seamless to players.
These were not theoretical challenges. Each one required deep system-level engineering, careful architectural planning, load testing, and continuous refinement.
Implementation and Strategy
Building the system required approaching it from multiple angles simultaneously: the networking layer, the backend architecture, infrastructure automation, data consistency, scale testing, and Unreal Engine integration.
Microservice Architecture and Distributed Backend
The backend ecosystem is fully microservice-driven, with each service owning a well-bounded domain: accounts, inventory, cosmetics, payments, matchmaking, progression, and real-time events.
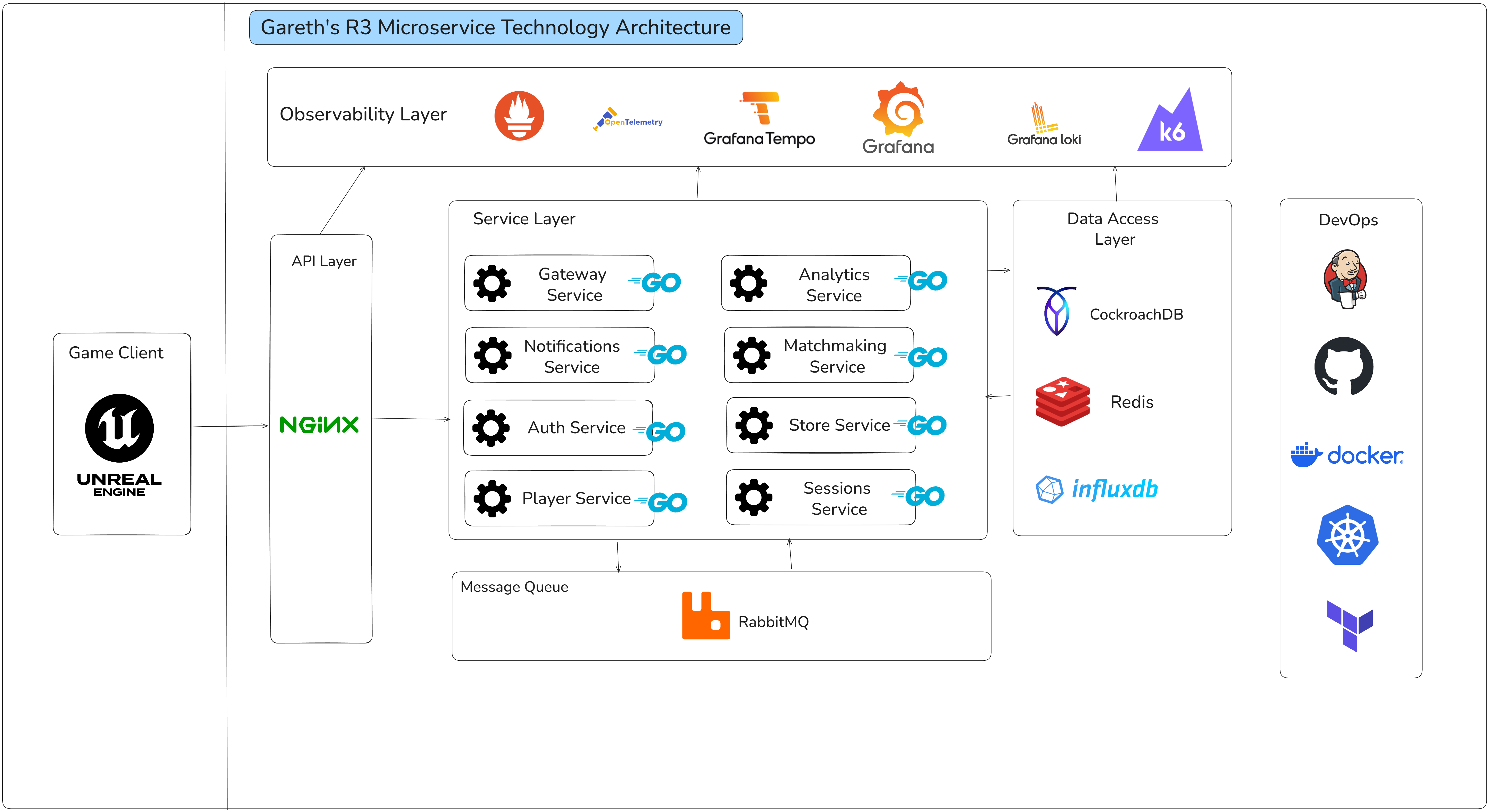
Services communicate through a combination of HTTP/gRPC for direct queries and RabbitMQ for event-driven interactions. This hybrid approach gives me low-latency synchronous paths when needed, and decoupled asynchronous patterns for cross-service updates.
Resiliency was a key priority. A failure in inventory should not impact payments. A failure in cosmetics should not break authentication. Each service is independently deployable, independently scalable, and built to gracefully handle upstream or downstream outages.
Load testing extended to the full infrastructure using K6, simulating real-world scenarios like burst traffic from thousands of players. This holistic suite tested sequential actions across endpoints, measuring latencies (P50/P90/P95/P99) and resource scaling, outperforming tools like JMeter.
Real-Time Gateway and Networking Layer
At the center of the runtime is a custom TCP gateway that handles bi-directional, low-latency communication with the Unreal Engine client. Building this from scratch gave me full control over serialization, packet shaping, connection lifecycle, authentication, and message routing.
Most importantly, I implemented the gateway in Go with a focus on memory efficiency, non-blocking I/O, and fine-grained control over goroutine scheduling. Through iterative load testing, profiling, and optimization, I reached over 10,000 authenticated concurrent connections on a single node, while sustaining more than 10,000 messages per second at under 10% CPU utilization and 500 MB of RAM.
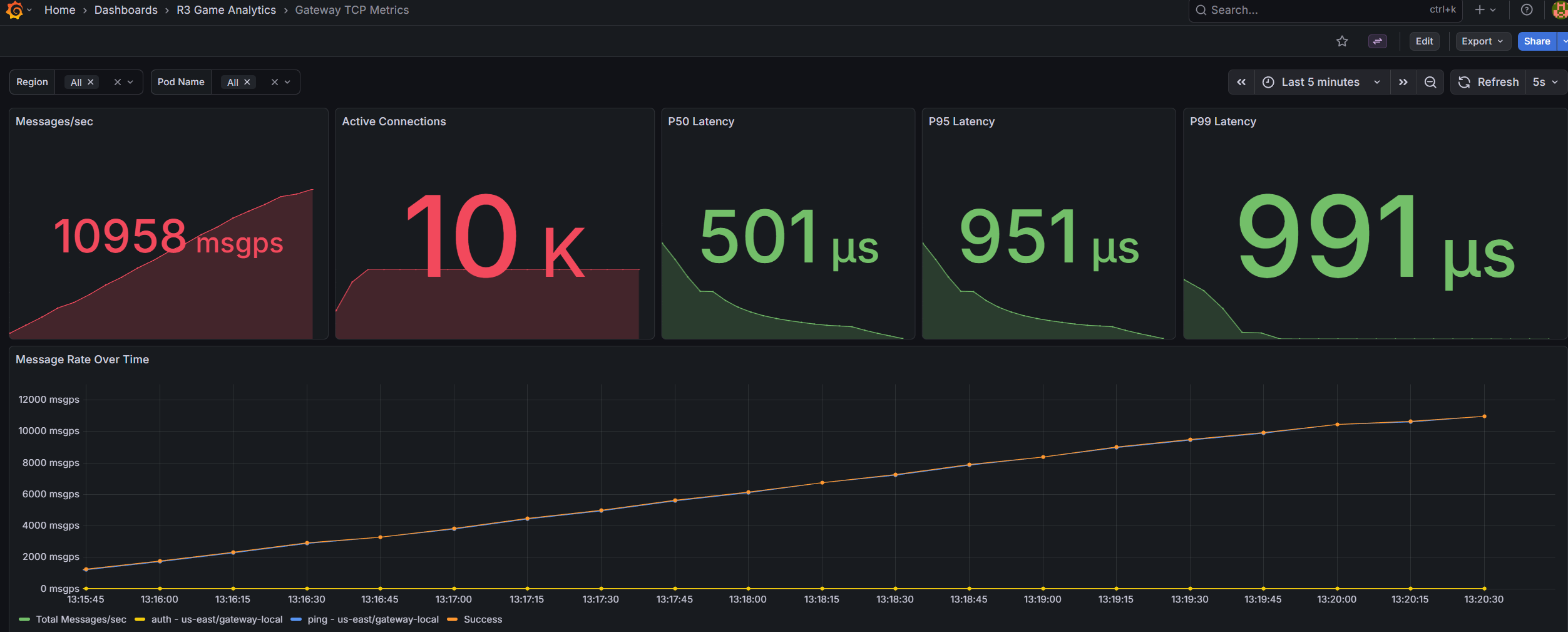
This required building my own custom TCP load-testing suite using Go. Existing tools were insufficient because they couldn’t simulate game-specific packet types, message patterns, or authentication flows. My custom suite allowed me to run realistic simulations: 10,000 simultaneous clients, each maintaining state, sending periodic packets, and executing request/response patterns mimicking a real live-service game.
The result was not just a gateway that worked, it was a gateway whose performance characteristics I deeply understood.
Infrastructure, Orchestration, and CI/CD
Every part of the system is containerized, built through GitHub Actions, and deployed through Kubernetes tested locally using minikube.
For Unreal Engine dedicated servers, I took a step further by building an automated Windows-based Jenkins pipeline capable of packaging dedicated server builds inside the official Epic Unreal Engine Docker image. This eliminated the traditional pain point of manually building Unreal Engine servers across machines.
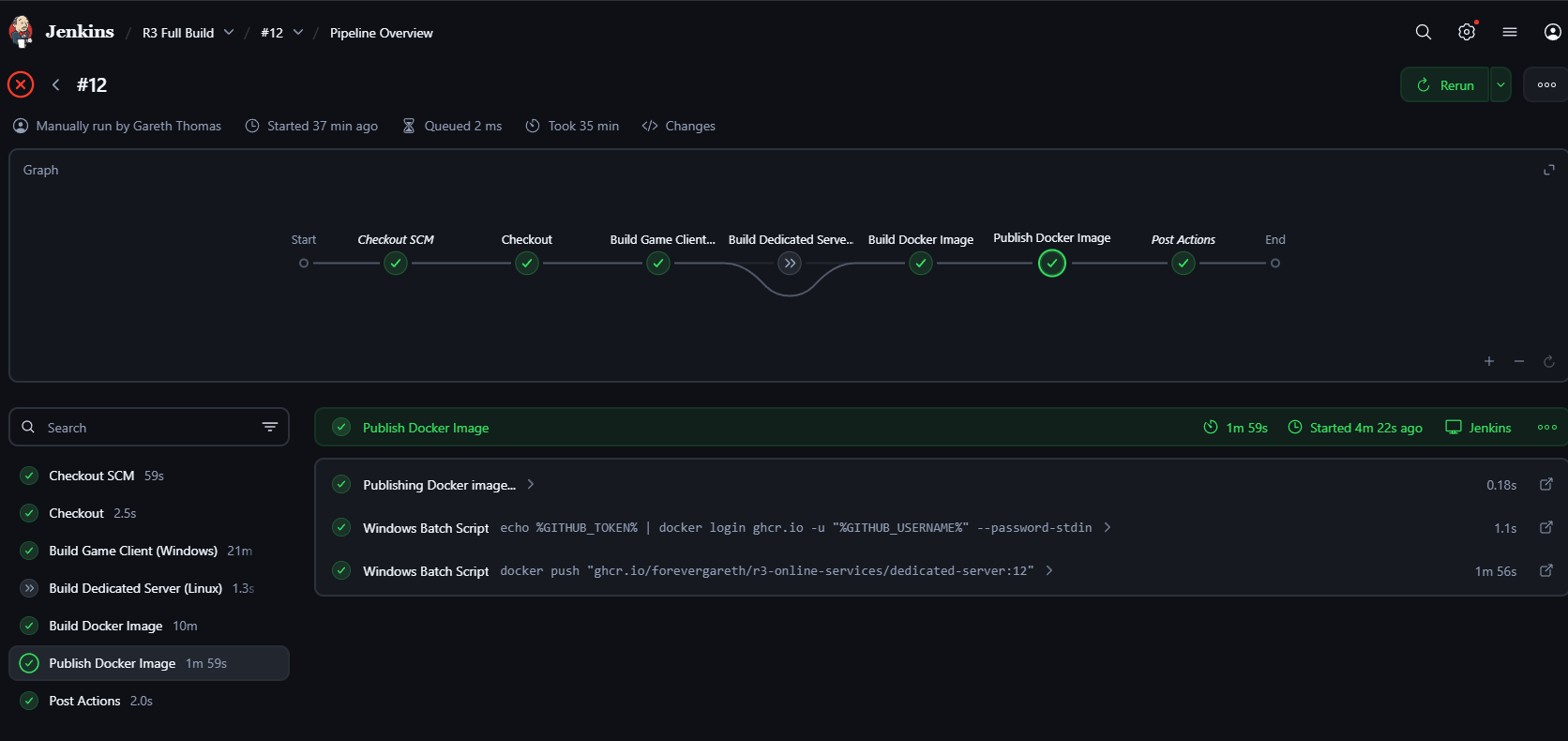
Once built, the images are published to GitHub Container Registry and can be deployed anywhere, even onto bare-metal nodes with minimal friction and Docker compatibility.
Terraform closes the loop by provisioning a single GKE Control Plane, Hetzner worker nodes, the observability stack, and networking infrastructure on demand. A full region can be deployed in minutes, not days.
Observability and Performance Profiling
Live-service systems fail if they cannot be measured. To match industry standards, I built an observability stack composed of Prometheus for metrics, Loki for logs, Grafana for visualization, and Tempo for distributed tracing.
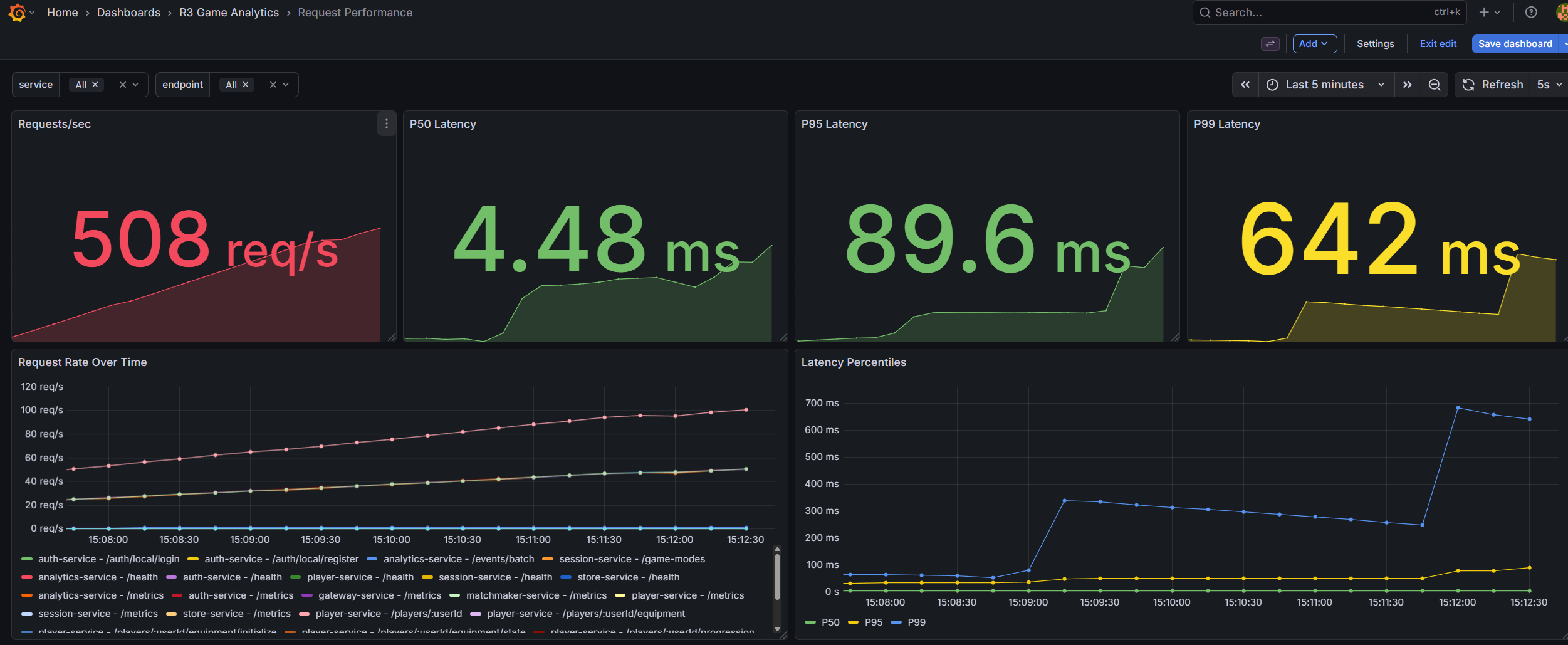
Paired with OpenTelemetry instrumentation across all backend services, I gained full visibility into request latency, error propagation, cache behavior, message queue throughput, gateway performance, and database query analysis.
This visibility became crucial when pushing toward higher concurrency or diagnosing bottlenecks in the TCP gateway under large simulated loads.
Global Scale, Data Layer, and Consistency Models
Live-service games demand a data layer that can deliver global scale, strong consistency, and high availability, without sacrificing the throughput required for real-time gameplay.
PostgreSQL, while battle-tested and performant, hits fundamental limitations when scaling globally. Sharding introduces operational complexity, cross-shard transaction coordination, and rebalancing nightmares. At global scale, you're left managing a fragile patchwork of read replicas, proxy layers, and application-level sharding logic.
I evaluated two technologies purpose-built for this problem: Google Cloud Spanner and CockroachDB. Both offer globally distributed, strongly consistent, horizontally scalable SQL databases. Spanner pioneered the space, but CockroachDB won out for several key reasons:
- Local Development: CockroachDB runs seamlessly in Docker, allowing me to develop and test multi-region behaviors on my local machine without cloud dependencies.
- Cost Efficiency: CockroachDB Labs offers significantly more affordable cloud tiers compared to Spanner's enterprise pricing, critical for an independent project.
- Postgres Compatibility: Near-complete Postgres wire protocol support meant my existing Go database tooling, migrations, and queries worked with minimal changes.
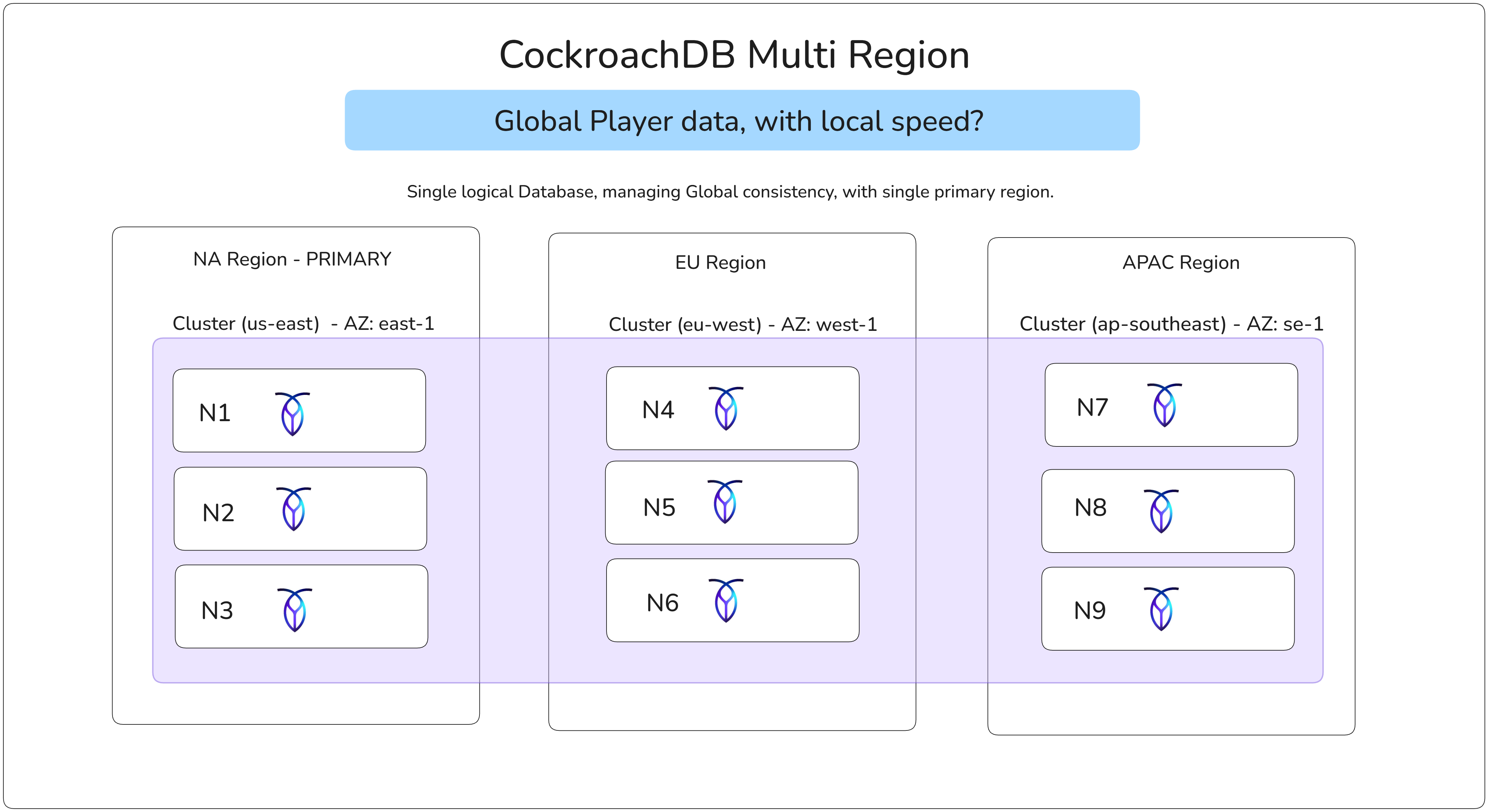
The architectural power of CockroachDB lies in its native multi-region primitives. I leveraged Global Tables and Regional Tables to make deliberate decisions about data locality:
- Global Tables for data requiring low-latency reads worldwide ie. cosmetic catalogs, store configurations, and game metadata. These tables replicate across all regions, ensuring any player anywhere reads local data instantly.
- Regional Tables for player-specific, high-write-throughput data ie. inventories, match history, progression state. By pinning this data to the player's home region, I minimized write latency while maintaining strong consistency guarantees.
This explicit control over data placement allowed me to optimize for the access patterns that matter: fast reads globally, fast writes locally. An European player's inventory updates stay in Frankfurt with single-digit millisecond commits, while the cosmetic store they browse is served from a local replica without cross-Atlantic round trips.
Unified Player Accounts and Authentication
Cross-platform identity is a common feature players come to expect for modern live-service games. They expect to link their Steam, Epic, PlayStation, or Xbox accounts and retain progression and purchases across devices.
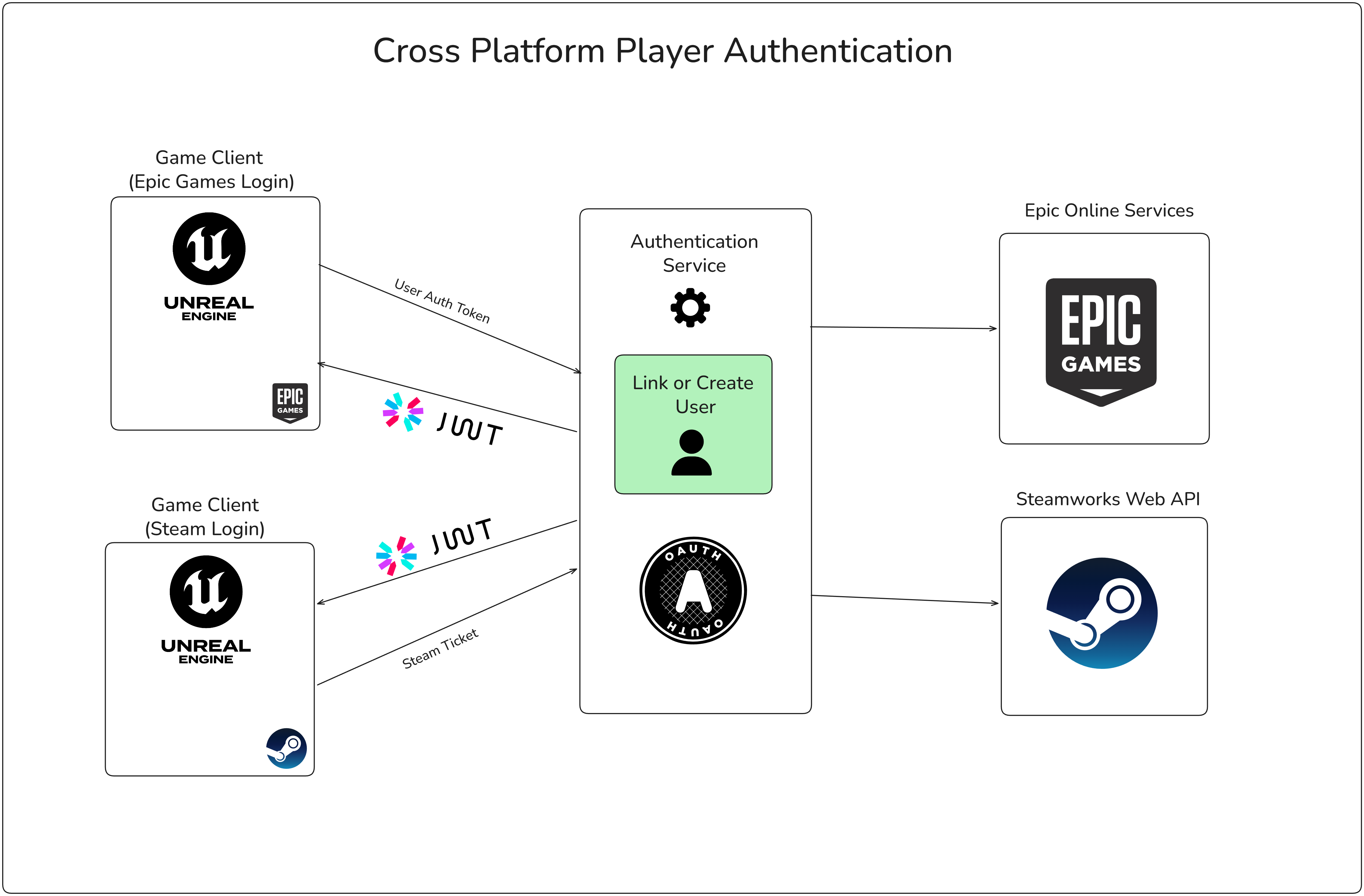
I leveraged Unreal's Online Subsystem abstraction to integrate with Steam and Epic Games identity providers. On the client side, this meant implementing platform-specific login flows that retrieve authentication tickets. On the backend, I built an OAuth 2.0-based account service that validates these tickets against platform APIs, issues JWT tokens, and manages account linking.
The account service handles several edge cases critical to production systems:
- Account Creation vs. Linking: First-time players automatically create accounts; returning players on new platforms can link to existing accounts.
- Fallback Authentication: Username/password login for development and testing environments where platform SDKs aren't available.
- Token Refresh: Short-lived access tokens with refresh token rotation to minimize exposure from compromised credentials.
This architecture ensures a player's identity, inventory, and progression persist regardless of which platform or device they use to play.
Microtransactions and Store Integration
Monetization infrastructure must be secure, auditable, and seamlessly integrated into the gameplay experience. I built a full store service backed by Stripe for payment processing.
The purchase flow works as follows:
- The Unreal client requests a checkout session from the store service via rest API's.
- The store service generates a Stripe Checkout URL with the selected item and the Unreal Client redirects the player to Stripe's hosted payment page.
- Upon successful payment, Stripe webhooks notify the store service, which publishes a fulfillment event to RabbitMQ while the various services consumes the event and credits the player's account.
- A real-time TCP notification is pushed to the player's game client, updating their inventory instantly.
Cosmetic items are defined as Unreal Primary Data Assets, enabling designers to manage item metadata, visuals, and categorization directly in the editor. The backend maintains ownership records, ensuring the client displays only what the player legitimately owns.
Progression and Equipment Systems
Progression systems must be server-authoritative to prevent cheating while remaining responsive enough to feel rewarding. I implemented an XP and leveling system where all state mutations occur on the backend.
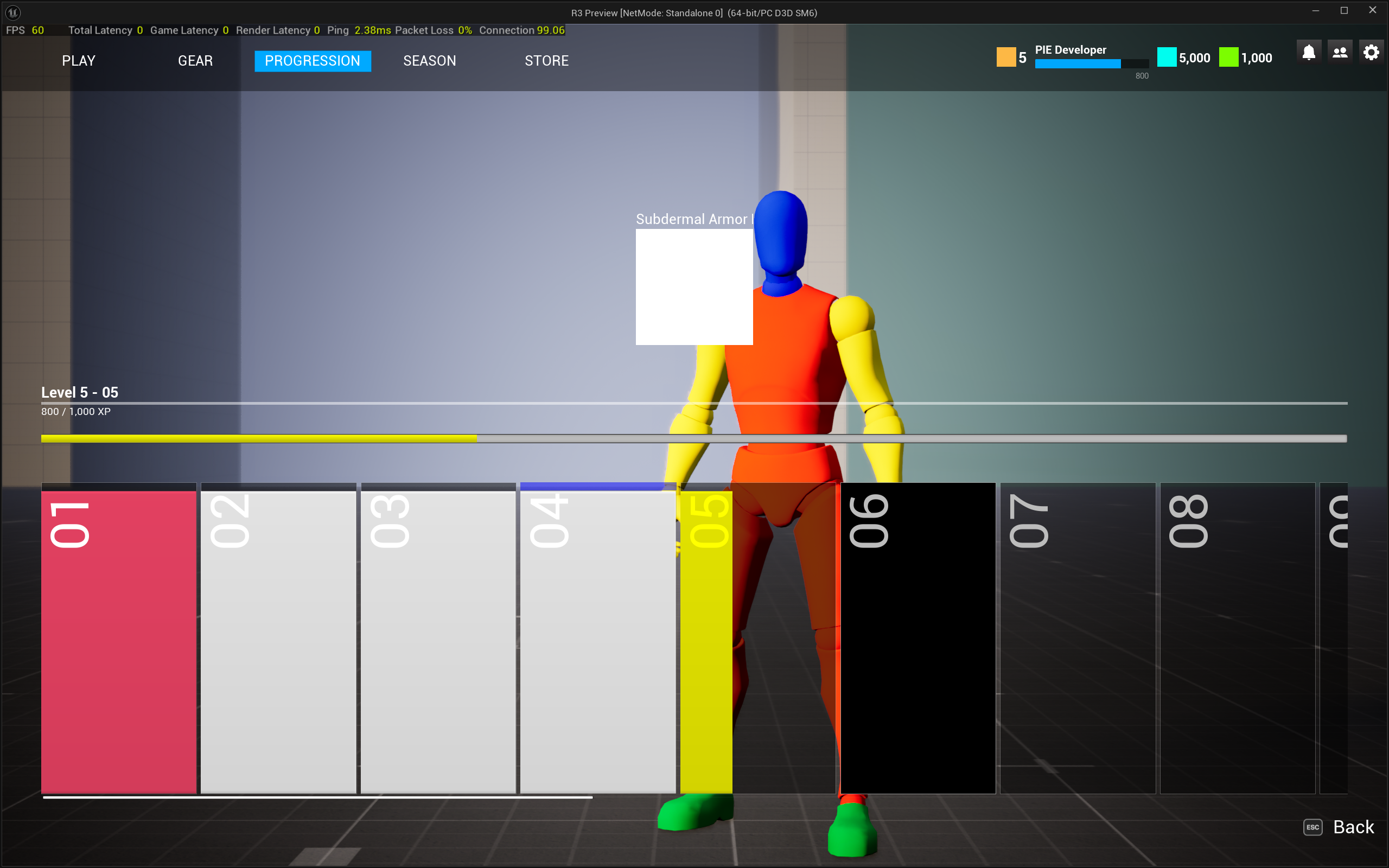
When a match concludes, the dedicated server reports match results directly to the player service via authenticated server-to-server API calls. The backend servers validates XP gains, level-ups, and unlocks rewards tied to the new level. These updates propagate to the player in realtime.
I built a CommonUI-based menu interface that displays:
- Current level and XP progress toward the next level
- XP requirements per level with visual progression bars
- Unlockable rewards at each level threshold
- Equipment loadout management with server-validated selections
This separation ensures that even if the client is compromised, progression state remains trustworthy. The client is purely a view layer for data owned by the backend.
Matchmaking and Dedicated Server Provisioning
Matchmaking and server provisioning are among the most operationally complex systems in live-service games. I designed a custom matchmaking system inspired by OpenMatch and Agones, but tailored for my infrastructure constraints.
The matchmaking service supports multiple provisioning drivers:
- Mock Driver: Returns fake server details for local development and unit testing.
- Docker Driver: Spins up dedicated server containers on-demand for integration testing and small-scale deployments.
- Kubernetes Driver: Provisions dedicated server pods in specific regions, enabling geographic matchmaking and regional scaling.
When a match is formed, the provisioner:
- Selects an appropriate region based on player region.
- Allocates a dedicated server instance with a randomly generated connection password.
- Assigns a dynamic port from the available pool.
- Returns connection details to matched players via the real-time gateway.
This architecture allows the system to scale from local development to multi-region production deployments without changing application code, only the provisioning driver configuration changes.
Conclusion and Takeaways
This project represents one of the most ambitious engineering efforts I’ve undertaken independently, and it reflects the exact type of work I want to contribute to professionally: large-scale online multiplayer systems, real-time gameplay networking, distributed architecture, and live-service operations.
Just as importantly, the project strengthend my architectural chops and product ownership. Asking the hard questions and balancing performance, reliability, cost efficiency, developer experience, and long-term sustainability.
This framework is not the final version; it is the foundation on which I plan to continue building. Over time, I intend to expand it to include social features, a more robust matchmaking system, and a seasonal progression, web dashboard for moderation and managing the content pipeline. Each step pushing the entire system closer to the demands of a global live-service title.
More than anything, it has reinforced my passion for creating high-performance online experiences and it has positioned me to meaningfully contribute to the next generation of multiplayer games.